Blockchain
Blockchain technology is one of the most promising and emerging technologies, but unfortunately considerable computing power is required where the technology is to be used to mine digital currencies – termed as ‘coins’. The essence of the blockchain is to offer storage to transactions in a ledger that can be trusted and without the influence of central authority. It is truly peer-to-peer; it doesn’t require controlling intermediaries to authenticate or to settle transactions and information among a network of interested parties.
It is basically an encrypted distributed database with the form of a chain of blocks interlinked using open-source digital protocols through cryptographic security, based on an immutable characteristic (consensus protocol = most hash power). Some Enterprise Blockchain solutions are either considering or have already implemented blockchain in their businesses. Examples are: JP Morgan, Volkswagen, British Airways, Maersk, Walmart, BP, Equinor and Shell, and the list goes on…
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a technology with three pillars:
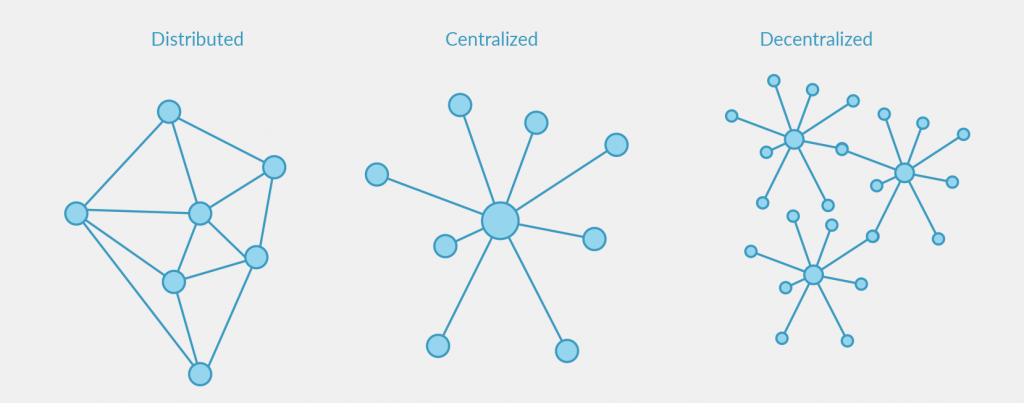
Decentralization – A mediator or intermediary is no longer required, as it is a disintermediation process. It is more collaborative, helping to prevent systemic failure, collusion, and more.
Transparency – It is completely traceable throughout each step of the chain process by any of the interested parties. Each block (list of records) also contains the hash1 (cryptography) of the previous block of the chain. In a blockchain, once a transaction is validated through a consensus protocol2, it is also committed to all ledgers in the network.
Immutability – Immutability means that the of a blockchain ledger may neither be changed nor altered. The consensus algorithm is responsible for verifying the transactions and for executing the validation of blocks. This mechanism relies upon on network consensus.
This technology was invented in 2008, and first used in 2009 through Bitcoin – a cryptocurrency. The concept is released as open-source software, which now is leading to its use in many other sectors. Blockchain solutions are being now implemented in many other industries, such as in: Healthcare, Education, Real estate, Food, Automotive, Government, Finance and for many other opportunities.

Top Blockchain important capabilities:
- More trust – The transaction ‘Blocks’ are time-stamped on the blockchain and are mathematically related to previous Blocks. They are irreversible and practically impossible to tamper with.
- The unique time stamp on the Block – eliminates the so-called ‘Double-spend’ problem.
- Enhanced security – There is no central point to be exploited.
- Improved transparency/traceability – It is a fully auditable and is a valid ledger of transactions. The transaction details are shared only amongst the participants involved in those transactions, and are fully traceable.
- Elevate agreements – Reduce settlement time from days to near-instantaneous.
- Boost analytics – It may be used to predict market uncertainties and trends. It is part of every phase, thereby becoming integrated into the system (not a separate function).
- Reduce costs/time – Reduce costs by removing overhead associated with middlemen and intermediaries.
- Estimable redundancy – Each node (computer/device) has a copy of the blockchain.
Quality Assurance
Quality is essential to customer trust in order to allow business to be done, and Blockchain can play a crucial role through the quality assurance processes. Blockchain is an extremely useful technology for addressing problems related to business processes and should be considered as part of a business plan for quality assurance. Blockchain is still in its infancy and nowhere near perfection, and nor will it completely remove the need for human interaction. In addition, it will not be effective if the records of the business process are incomplete or inaccurate and it will not fix any bad data. Quality specialists will always remain an essential component of the business offering.
Blockchain has an immediate reactive nature, and organizations need to have proactive solutions that prevent errors or faulty product/services from happening.
Therefore, regular audits are essential to create accountability throughout your quality assurance systems and processes to ensure that they are at excellence level or minimum expectations as applicable. Quality assurance testing becomes essential in all applications of blockchain to ensure that the technology works smoothly delivering the desired benefits.
Blockchain improves solutions by preventing data from being altered retroactively, ensuring the verifiability and integrity of transactions. This can give to Quality assurance more accuracy and the absolute prevention of data manipulation. It allows both buyers and sellers to know who exactly they are doing business with. It has the potential to deliver greater efficiency, reliability, and high-quality data to improve business, but it does not replace quality, or the value of the data contents, nor prevent other problems from occurring. Without the appropriate limits, values, procedures, and quality methods, it is most likely not evolve to its best potential.
The ISO standards will benefit from this new technology through the standardization of blockchains and distributed ledger technologies to support interoperability and data interchange among users, applications, and systems. ISO is working on a series of blockchain and DLT (distributed ledger) standards ISO/TC 307 and other Blockchain and distributed ledger technologies. The plan is to have the first standards to be potentially released in 2021.